- 979-485-9287
- office@bvallergy.com
-
 979-251-7804
979-251-7804
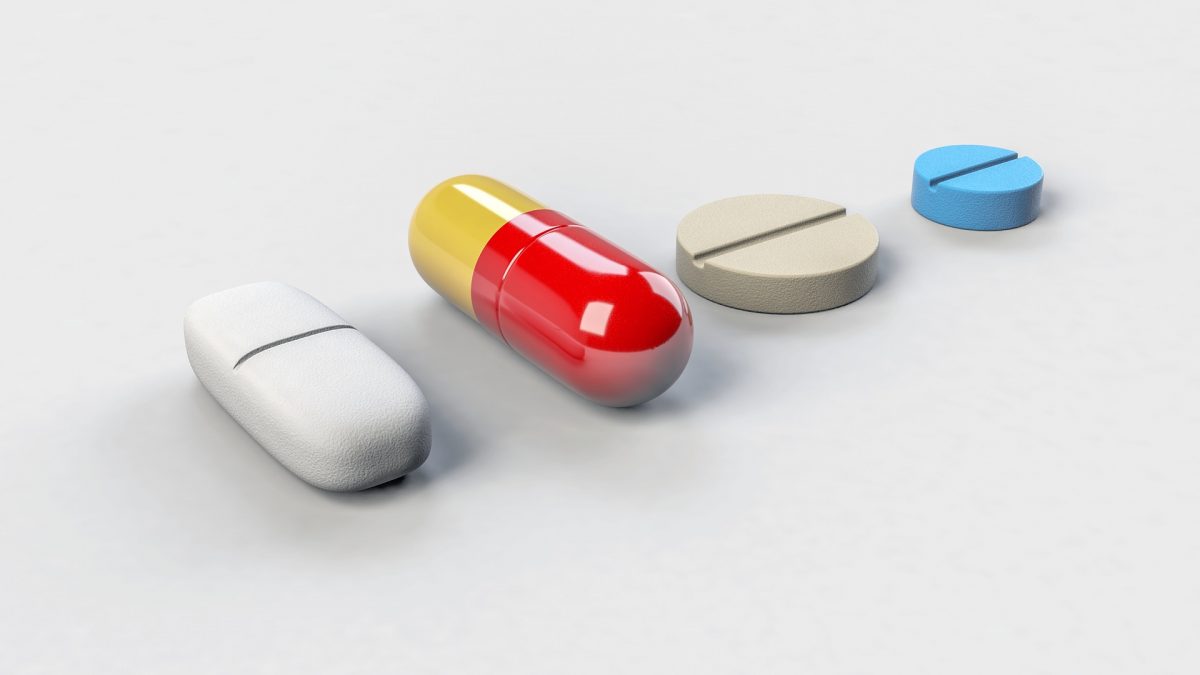
Best Antibiotics to Treat Sinus Infection

Signs of Sinus Infection
December 5, 2018
What You Didn’t Know About an Allergist
December 18, 2018Roughly 30 million adults in the United States (11% of the adult population) are diagnosed with sinusitis, according to research done by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
Some of them may choose to have no treatment and wait for their congestion to subside, while others may contact their physicians to prescribe their best medication for sinus infection. Doctors may recommend taking antibiotics, which can help alleviate pain and provide symptomatic relief.
However, there are many types of antibiotics your doctor may prescribe, which is the best antibiotic for sinus infection in adults. We’re here to help you understand the differences between each one!
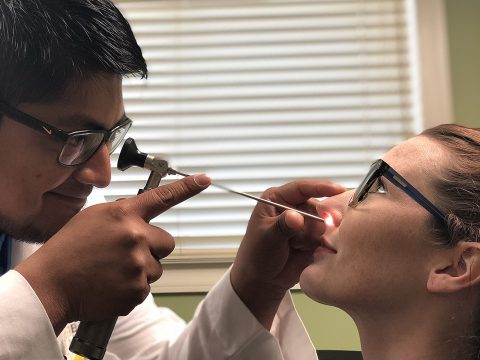
What is Sinus Infection?
Medically known as rhinosinusitis, Sinus infection or Sinusitis is an inflammation or swelling of the tissue lining the sinuses. Healthy sinuses are filled with air. But when they become blocked and filled with fluid, germs can grow and cause an infection. It occurs when your nasal cavities become infected, swollen, and inflamed. Sinusitis is usually caused by a virus and often persists even after other upper respiratory symptoms are gone. In some cases, bacteria, or rarely fungus, may cause a sinus infection.
What are Antibiotics?
Antibiotics are defined as any substance that inhibits the growth and replication of a bacterium or kills it outright, according to an article published by the Microbiology Society. It is a type of antimicrobial designed to target bacterial infections on or within the body.
Diseases that are caused by bacteria are usually treated with antibiotics and are highly effective in preventing the bacteria from spreading. Some antibiotics are used to attack a wide range of bacteria while others are highly specialized to target only certain bacteria. It’s important to note that antibiotics are used to treat bacterial infections and will not work for viral infections.
Why are Antibiotics Important?
Antibiotics are one of the most common classifications of drugs used to treat bacterial infections. Since their introduction to the world of medicine, they have helped treat countless people, especially those with infectious diseases.
Antibiotics are very crucial during surgeries and are used to prevent patients from getting any infections from the cut. Without antibiotics, there is a higher chance of blood poisoning and the more complicated surgeries would not be possible to perform.
What are the Best Antibiotics for Sinus Infection do Doctors Prescribe For You?
There are many antibiotics that your doctor or physician may prescribe to help treat your sinus infection. Some of these may even be familiar to you.
- Amoxicillin – This drug is commonly used to treat acute and uncomplicated bacterial sinusitis. This is taken in 3 or 4 divided doses daily for more effective results.
- Cefaclor – This drug is usually used to stop the growth of bacteria and is administered orally. If the patient has more severe infections, doses may be doubled.
- Sulfamethoxazole – This is an antibacterial medication used to treat infections that occur more frequently on people with a weakened immune system. This drug should only be taken according to your health care provider’s instructions.
- Azithromycin – This drug is also used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections which include respiratory infections, ear infections, skin infections, and sexually transmitted infections. Azithromycin contains ingredients that may cause an allergic reaction. Consult your doctor for more details.
- Clarithromycin – Just like Cefaclor, this drug is usually recommended to stop the growth of bacteria. This can be taken orally as a pill or liquid.
- Loracarbef – This is a synthetic oral antibiotic that prevents bacteria from multiplying. This drug is usually taken twice a day for more effective results.
- Amoxicillin-clavulanate (Augmentin) – This drug is a powerful antibiotic that is used to treat a wide variety of bacterial infections such as:
- Sinus Infection,
- Urinary Tract Infection and kidney infections
- Pneumonia,
- Ear, nose, skin and throat infections
- Tonsillitis and more
- Ciprofloxacin (Cipro) – This drug is used to treat conditions including urinary tract infections, specific types of infectious diarrhea, bone and joint infections, respiratory tract infections, typhoid, and other forms of bacterial infection.
- Trimethoprim (Bactrim) – This drug is the brand name for a medication that is a combination of two antibiotics: trimethoprim and sulfamethoxazole that is used to treat bacterial infections. Bactrim works by preventing the growth of bacteria.
These antibiotics are effective in treating sinus infection, however, these drugs do carry side effects. You should only be taken according to what your doctor or physician has prescribed. Always follow their instructions to achieve the best results.
When Do We Need Antibiotics for Sinus Infection?
Antibiotics are not needed for many sinus infections, but your doctor can decide if you need an antibiotic. You doctor may recommend antibiotics if:
- You have symptoms of a bacterial infection and you have not gotten better after 10 days, even with home treatment.
- You have severe symptoms such as severe headache or facial pain, or you have other problems, such as pus forming in your sinus cavities.
- You have had sinusitis for 12 weeks or longer (chronic sinusitis).
- You have a fever longer than 3-4 days.
- Your symptoms get worse after initially improving.
Most sinus infections usually get better on their own without antibiotics. When antibiotics aren’t needed, they won’t help you, and their side effects could still cause harm. Side effects can range from minor issues, like a rash, to very serious health problems, such as antibiotic-resistant infections and C. diff infection, which causes diarrhea that can lead to severe colon damage and death.
Most Frequently Asked Questions
What are the antibiotics used for a sinus infection?
The most common is Amoxicillin which is effective against most strains of bacteria. Other prescription medicines for sinus infection include Cefaclor, Sulfamethoxazole, Azithromycin, Clarithromycin, and Loracarbef.
How to treat a sinus infection without antibiotics?
Before you consider antibiotics, a sinus infection can be treated without leaving at home. Some of the home remedies to treat a sinus infection without antibiotics include:
- Keep your sinuses hydrated to help relieve pressure. One good way is to expose your sinuses to steam.
- Drink plenty of water.
- Essential oils like eucalyptus and peppermint oils may help open the airways and ease congestion.
- Apply warm and cold compression alternately to relieve sinus pain and pressure.
- Eat healthy foods – colorful fruits and veggies – that boost your immune system. These foods contain lots of vitamin C to fight off viruses.
- Get plenty of rest for your body to heal and fight the infection.
When to get antibiotics for a sinus infection?
Your doctor may prescribe you antibiotics if you are not relieved from initial treatments and have more concerning symptoms like worsening headache, fatigue, and sinus pain. The longer the symptoms last, the more likely you need an antibiotic.
Dr. Paul Jantzi, a board-certified allergist and immunologist, provides allergy treatments in Texas with office locations in Bastrop, Brenham, College Station, Columbus, Giddings, and La Grange.
You can contact him at any of the Brazos Valley Allergy & Asthma Clinics for professional allergy, asthma, and immunology services to patients at six locations throughout the Brazos Valley. They provide the best care and affordable antibiotics for patients.
REFERENCES:
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Microbiology Society
Richmond ENT
PlushCare
MedicineNet
MedlinePlus
AIDSinfo
WebMD